Connecting to the Cloud
Before sending data to Ubidots, you need to set up your device and integration within the HARDWARIO Cloud. This tutorial will walk you through each step required to connect via a webhook connector. If you have not yet completed the initial Cloud setup steps, you can follow the instructions here: HARDWARIO Cloud Documentation.
Step-by-Step Instructions
-
Create a New Connector
To establish communication with Ubidots, go to the
Connectorssection in the left-hand menu.
Click+ New Connectorand configure the following:
•Name– give your connector a name
•Type– selectWebhookfor Ubidots integration
•Trigger– chooseData
•Tag– assign the tag you created earlier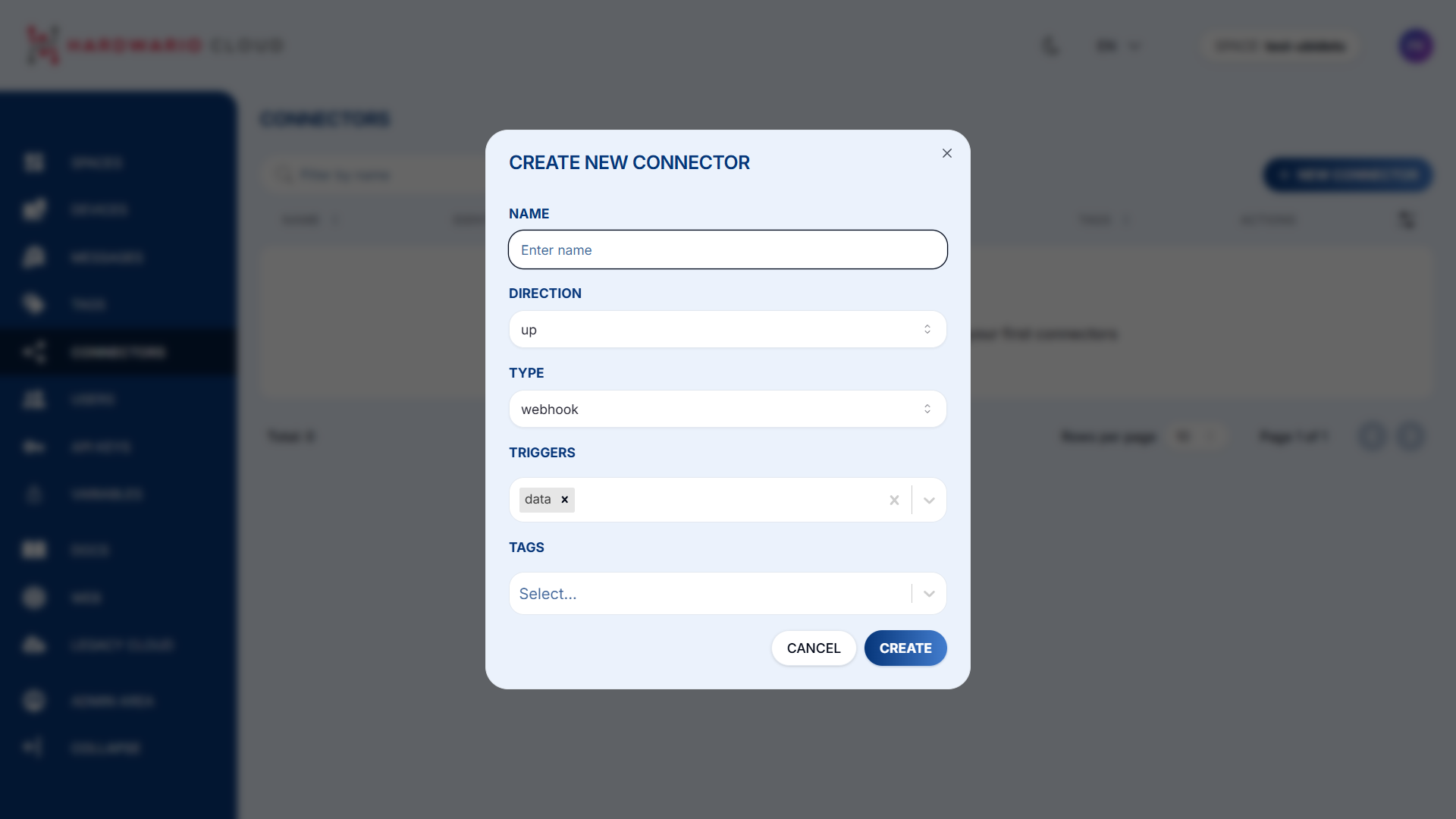
-
Transform Data for Ubidots Format
Ubidots requires a specific data format. You need to adjust your device data using a transformation code.
In the connector page, scroll down to theTransformationsection and click the magnifying glass icon 📄🔍 to open the code editor.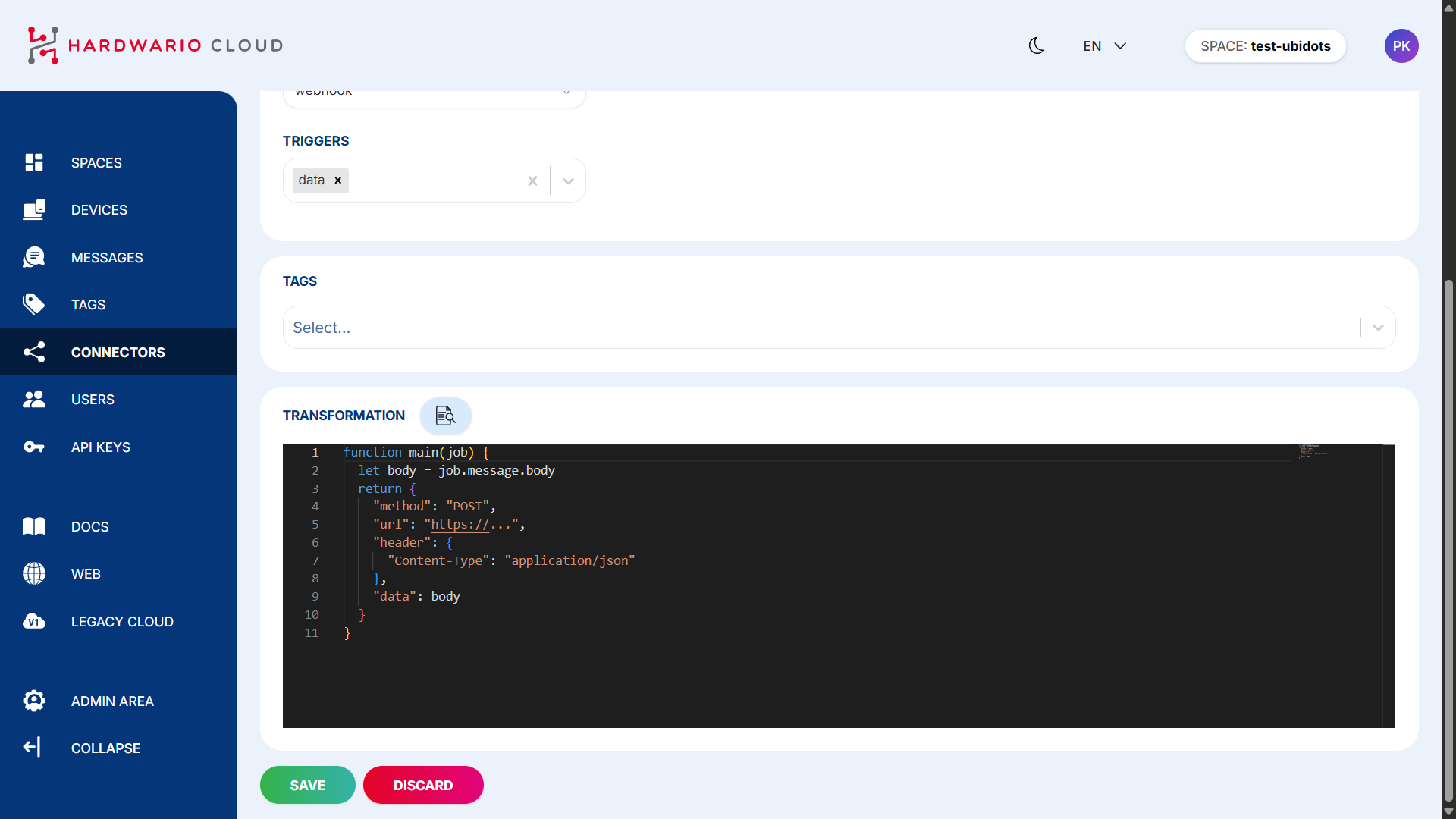
-
Insert the Transformation Code
Add the transformation logic that converts incoming data to a Ubidots-compatible format.
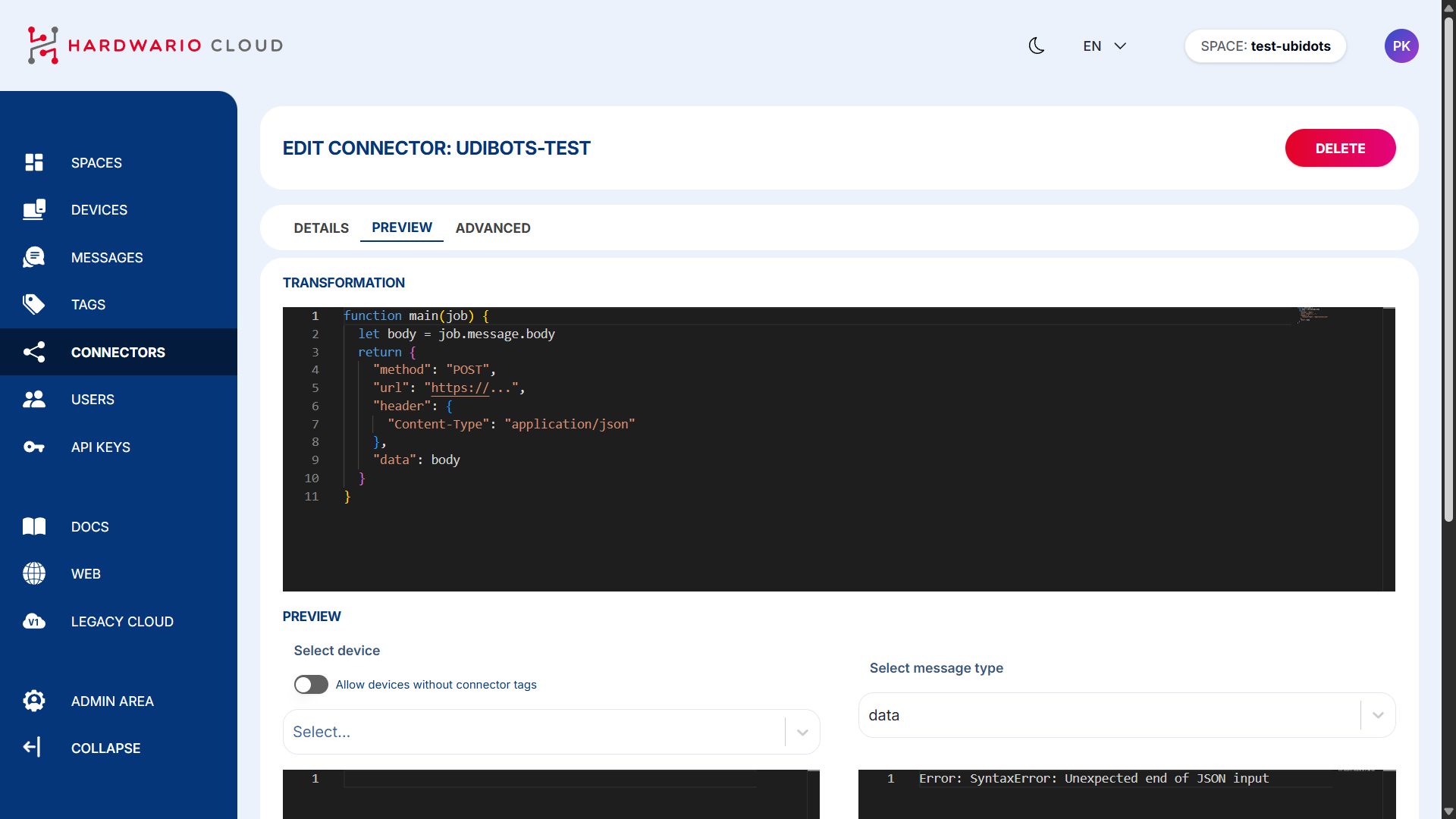
Example of transformation code here:
-
Set Ubidots Token in Headers
Make sure to include your Ubidots device token in the header of the transformation code to authorize data transmission.
-
Assign Devices to Connector
Scroll down and select which devices (with the matching tag) should be connected.
On the left side, you'll see incoming data from the device.
On the right side, you'll see the transformed data being sent to Ubidots.
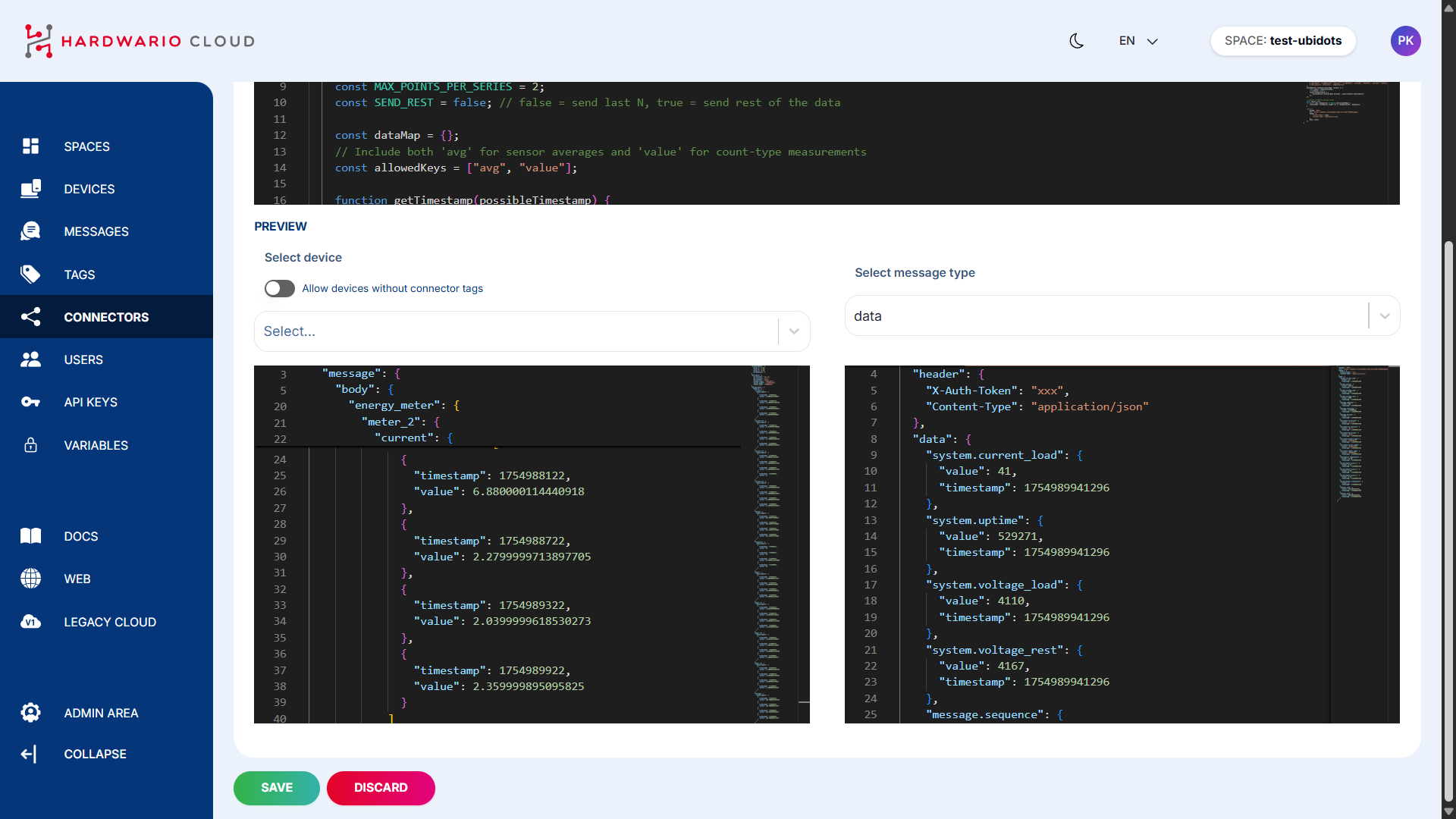
Once everything is properly configured, your device’s data should begin flowing into Ubidots automatically.
Video Tutorial
If you need further assistance or a visual demonstration of the process described in this guide, consult the Video Guide.