The Things Stack
Introduction
The Things Stack (TTS) is a modern and scalable LoRaWAN® Network Server designed for secure, reliable, and flexible IoT connectivity. Developed by The Things Industries, it powers both public and private LoRaWAN networks, offering advanced device, gateway, and application management features suitable for enterprises, developers, and service providers.
Key Benefits
- Enterprise-grade security – TTS implements end-to-end encryption, secure device provisioning, and multi-tenant architecture to protect data and ensure compliance.
- Scalability and reliability – Built for large-scale deployments, with clustering, redundancy, and multi-region support.
- Flexible deployment options – Available as a managed cloud service, private cloud, or on-premises installation.
- Interoperability and open standards – Fully compliant with the LoRaWAN® specification and integrates easily with existing IoT platforms via MQTT, Webhooks, or APIs.
What You Can Do with TTS
With The Things Stack, you can deploy and operate a complete LoRaWAN infrastructure — from device registration and gateway management to data routing and integration with third-party systems.
You can build and scale IoT applications for smart agriculture, asset tracking, energy management, logistics, or industrial monitoring, while keeping full control over your network and data.
The Things Stack provides the foundation for professional LoRaWAN networks — secure, scalable, and interoperable. Whether you’re building a private IoT solution or operating a global deployment, TTS gives you the tools to manage your devices and data with confidence.
Configure The Things Stack
In this guide, you will configure The Things Stack by adding gateways and registering end devices. It shows how to work with LoRaWAN settings, assign network parameters, and properly register devices within your TTS application environment.
👉 Step-by-step guide sections:
-
Gateways: https://docs.hardwario.com/apps/the-things-stack/tts-configuration/tts-gateways
-
End Devices: https://docs.hardwario.com/apps/the-things-stack/tts-configuration/tts-end-devices
LoRaWAN Network
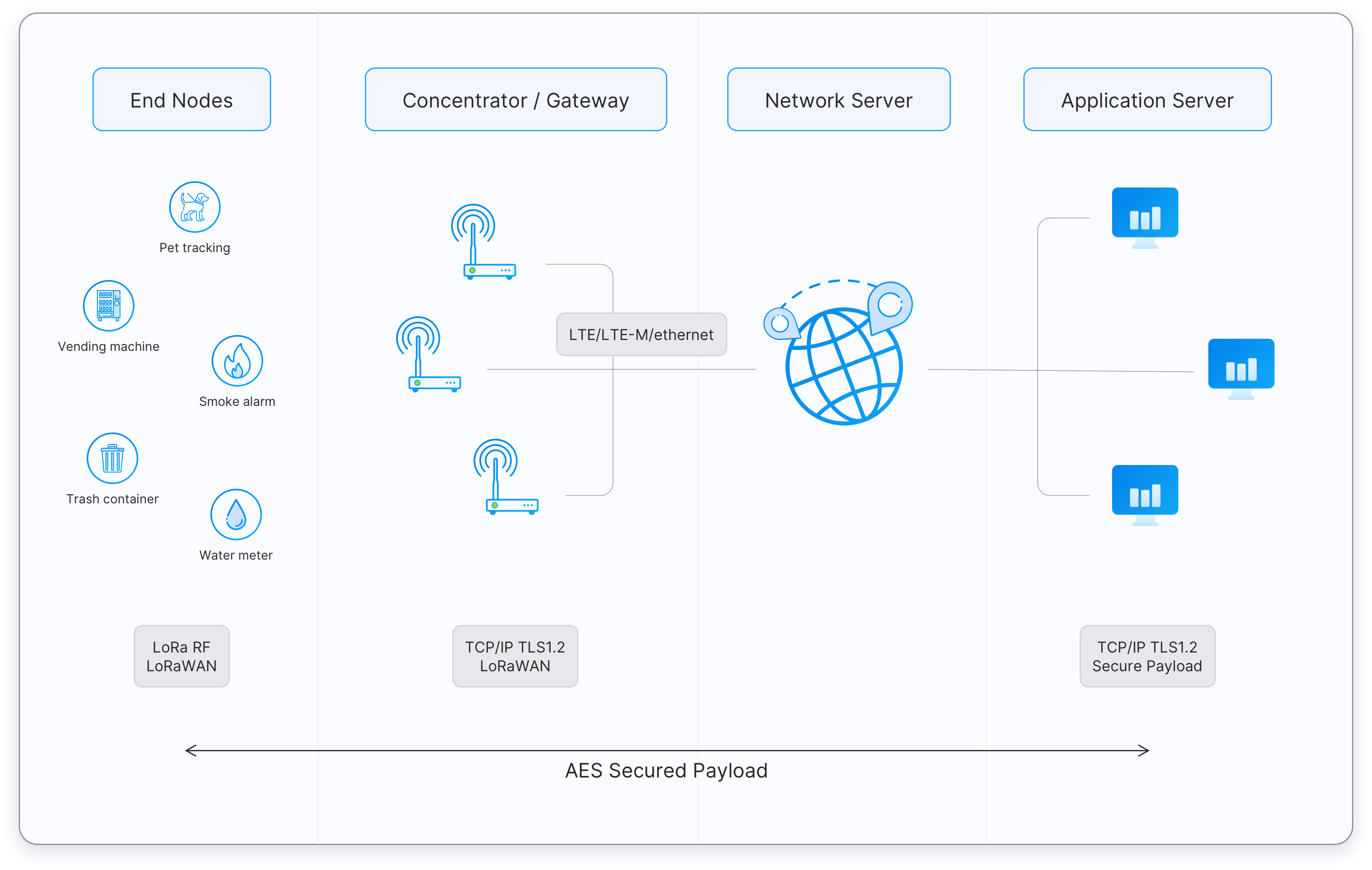
LoRaWAN is a low-power, wide-area network (LPWAN) protocol built on top of the LoRa modulation. It is specifically designed for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. LoRa modulation is based on chirp spread spectrum (CSS), which enables long-range connectivity, resistance to interference, and operation with very low power consumption.
Devices and Gateways
End devices, such as sensors or actuators, are typically battery-powered and communicate using LoRa modulation. These devices transmit messages using an ALOHA-based protocol, meaning they send data whenever they need to, and any gateway within range can receive it. Gateways then act as packet forwarders, relaying received messages over IP (via Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or cellular) to the network server.
Network Server
The Network Server is the central intelligence of a LoRaWAN network. It:
- Authenticates and manages devices.
- Deduplicates messages when several gateways receive the same transmission.
- Determines the best gateway path for downlinks.
- Enforces end-to-end security using AES-128 encryption.
Application Layer
After processing, the Network Server forwards the messages to the Application Server. Here the data can be visualized on dashboards, integrated into cloud applications, or used to trigger automation workflows.
Topology and Use Cases
LoRaWAN follows a star-of-stars topology, where end devices connect to multiple gateways, and those gateways are connected to a central server. This architecture is ideal for applications that require long range, low power consumption, and small, infrequent messages. Typical use cases include smart agriculture, smart cities, asset tracking, utility metering, and industrial monitoring.
LoRaWAN Network Topology